Structures on Mars - Housing Unit
The goal of building a structure on Mars is to create a shelter for a team of 4 during 1 year. The housing unit needs to ensure the safety of the team facing the Mars adversities and to ensure that the mental health of astronauts is not compromised. For this purpose, the design of the housing unit on Mars will consist of 3 elements with different objectives and will be built using mainly technology associated with 3D printing:
- Laboratory and Work Module;
- Transition Module - House - Work;
- Housing Module - Leisure.
To ensure an acceptable thermal behavior for the housing module, some thickness values of this module were limited to a minimum value. The recommended thermal comfort characteristics were accepted as recommended average values in Europe. Assuming that, in addition to the thickness of 3cm of polyethylene, a thermal insulation layer of basalt fiber of 3.5 cm will also be placed, it is possible to calculate the minimum thickness of the moisture ABS and Basalt Fiber.
Color
The structural component of the house will be composed by a mix of composite ABS (colorless) polymer and basalt fibers. That means that, seen from the outside, the housing module will have a color according to the image below.
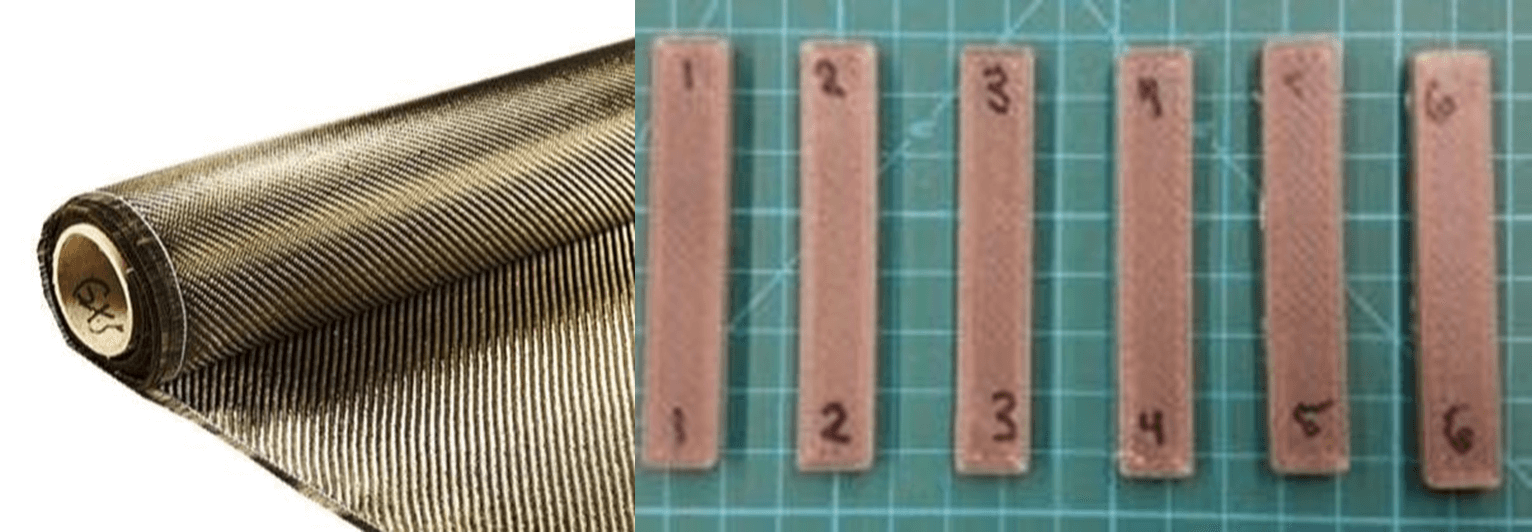
1 Color of basalt fiber and texture of ABS and basalt fiber moisture
In the structure there are two types of wall, 1-walls that divide the interior from the exterior and 2-walls that function as partitions inside the house. Type 1 walls are constituted, from the inside out, by a layer of polyethylene - 3cm, which can have any color, a layer of insulation of basalt fiber - 3.5 cm and a layer with a moisture of ABS and basalt fiber - 15 cm.
Type 2 walls consist of a 1.75 cm layer of basalt fiber insulation on each side, 1 layer with 15cm of moisture ABS and basalt fiber. The interior can be coated with the desired color.
Modules
As mentioned above, the housing unit consists of 3 modules: Housing Module, Laboratory and Transition Module.
The Laboratory and Housing module, are, outwardly, equal, only differ in the arrangement of the partition walls. Each of these modules consists of a cylinder with 14 meters in diameter and 2 meters high. On top of this cylinder is a spherical dome with a maximum height of 6 meters. The displacement module is only a cylinder with a radius of 2.4 meters, cut and lying down, which joins the laboratory module with the housing module.
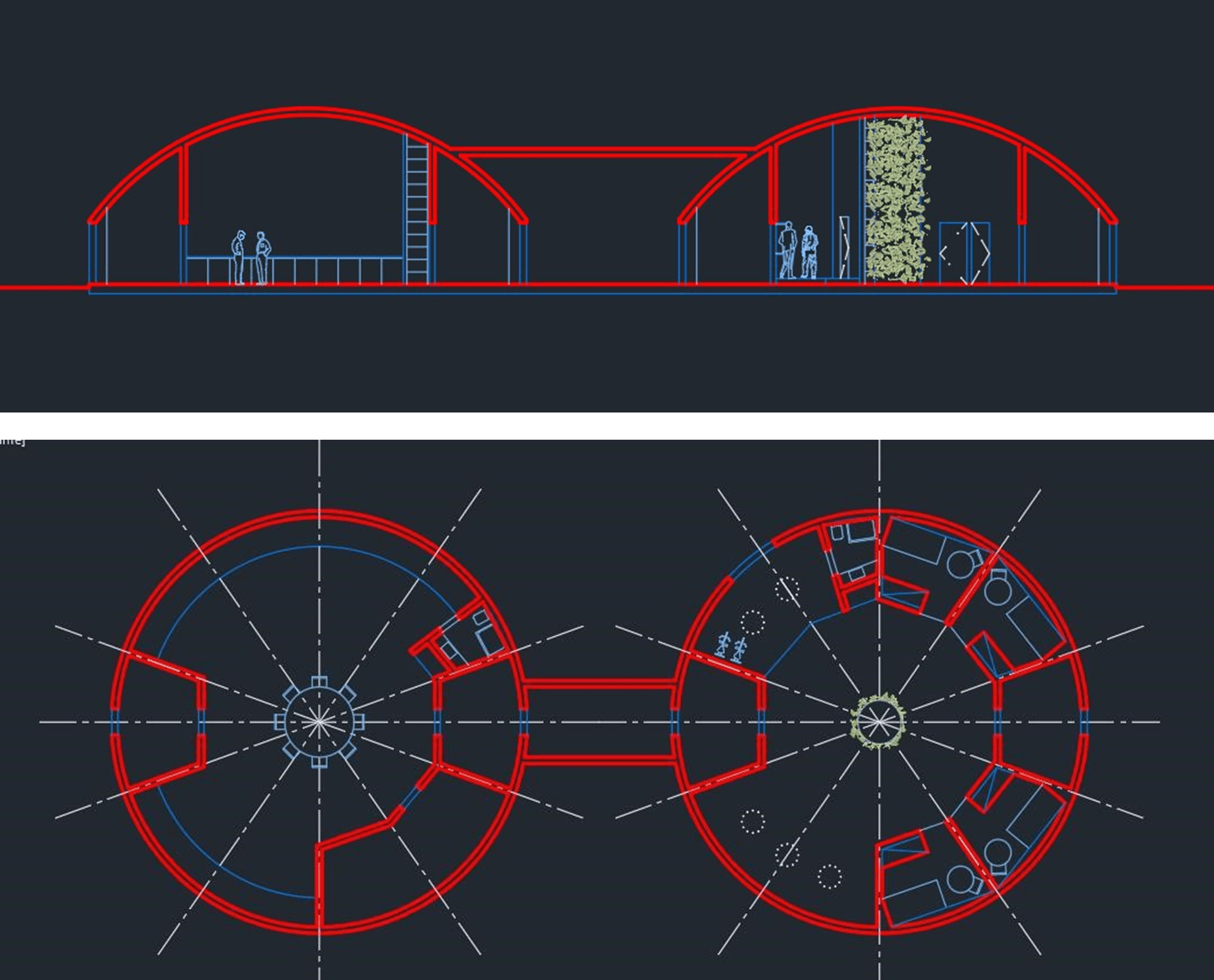
2 Cut and Plan view
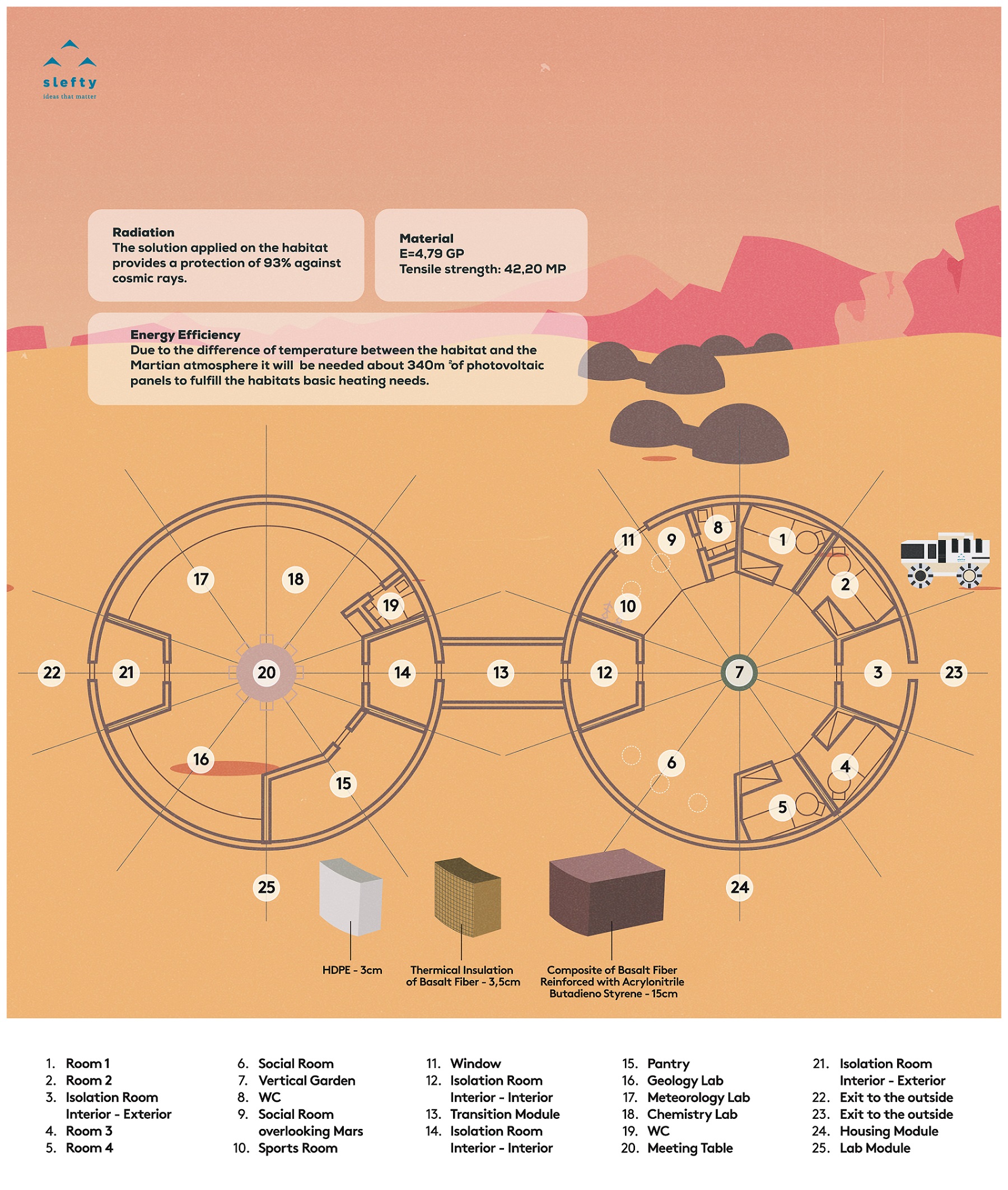
Each module has two entrances/exits that connect to isolation divisions. This division allows astronauts to equip/disequip each other when returning/departing from missions to Mars. The housing module has 4 bedrooms, 1 toilet and a common space. There is still no need to have a kitchen, however, it can be implemented in the future without compromising the design of the structure. The housing module has a vertical center garden that occupies the entire height of the module. In addition, it contains two living spaces and a window overlooking Mars, whose dimensions cannot exceed 1.5 meters. On a night of less radiation, astronauts can contemplate the sky of Mars in the safety of their housing modules. The window must be equipped, in the remaining days, by a device that protects residents from radiation. In the same space there are two bicycles and other sports equipment, which will allow astronauts to maintain their physical forms and relieve stress. The other empty space, below, will serve as leisure space and will have to contain storage.
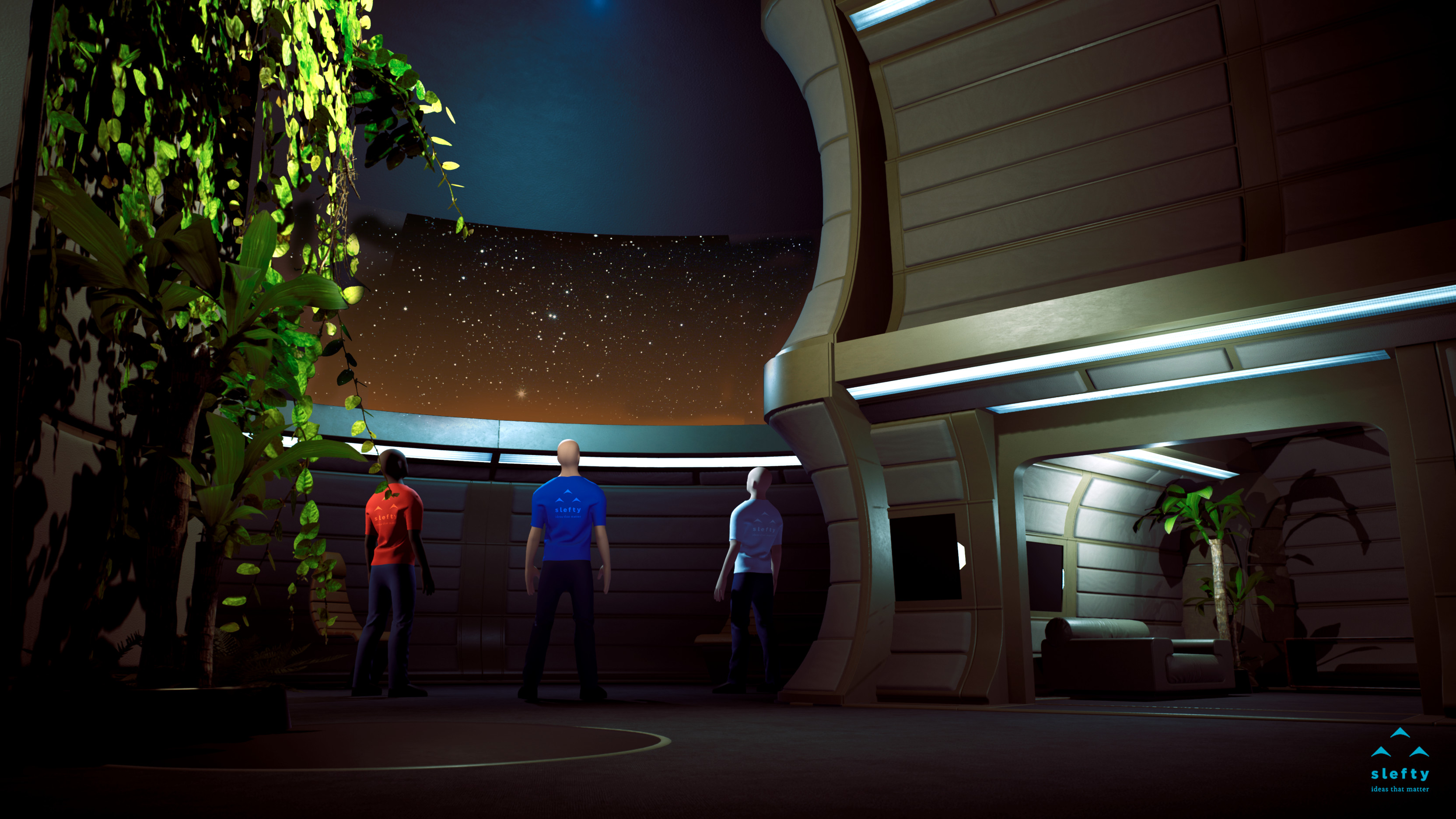

3 Interior view of the housing module
The laboratory module, in addition to the isolation rooms, has a toilet and some storage, if the housing module is inoperable. In the rest of the space, it has in its radius a table of 1 meter long that will allow to divide laboratory according to the areas of study of the mission: geology, biology and meteorology. In the center of the module is a meeting table. The laboratory will be equipped with technical equipment dedicated to each area of study.
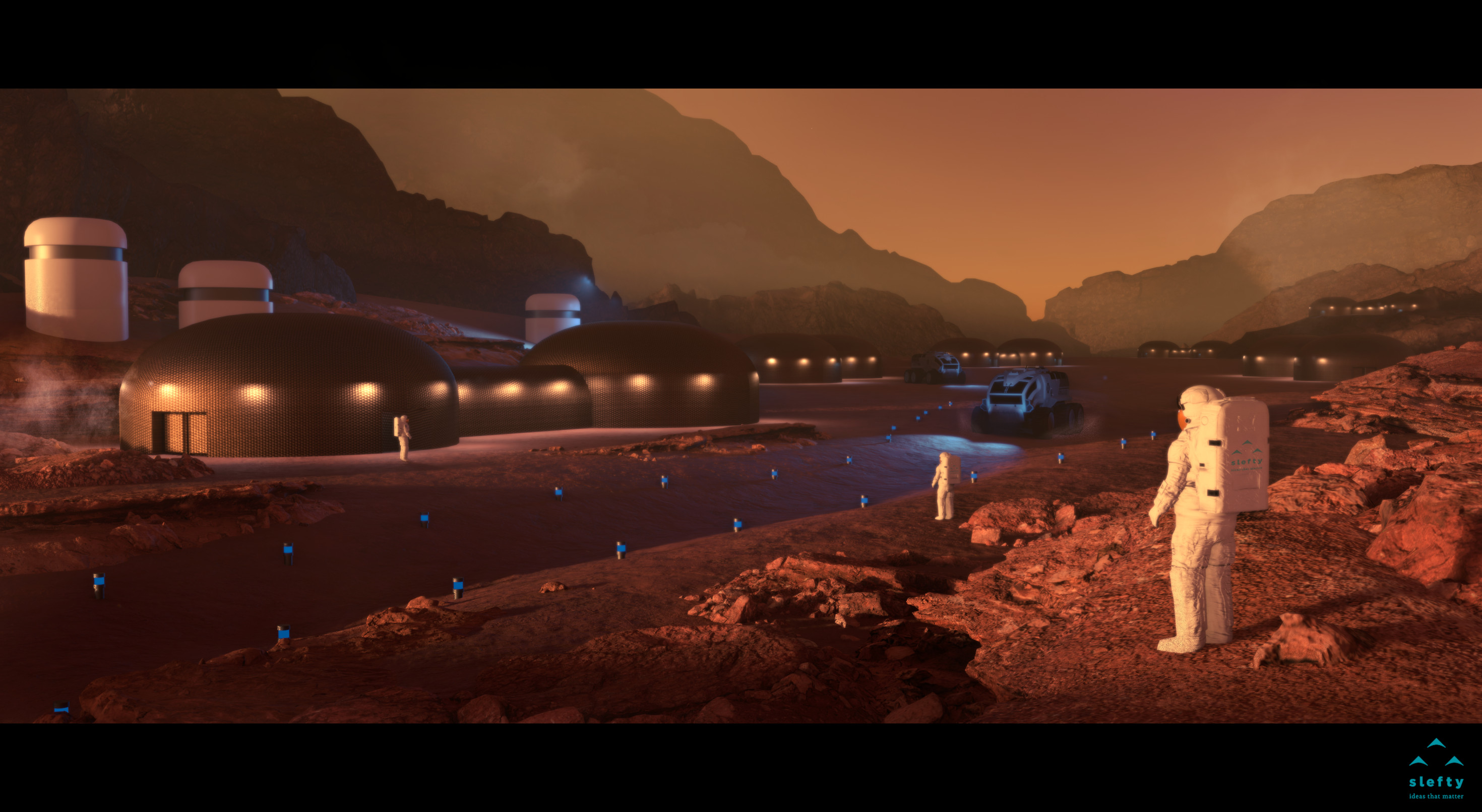

4 Exterior view of the housing module
Mechanical behavior of the housing module
By applying the total loads from the pressure difference in the walls, which separate the interior of the housing and the exterior, we were able to simulate the behavior of the structure on Mars, with the design and materials selected. In the images, it is represented the stress values on the materials.
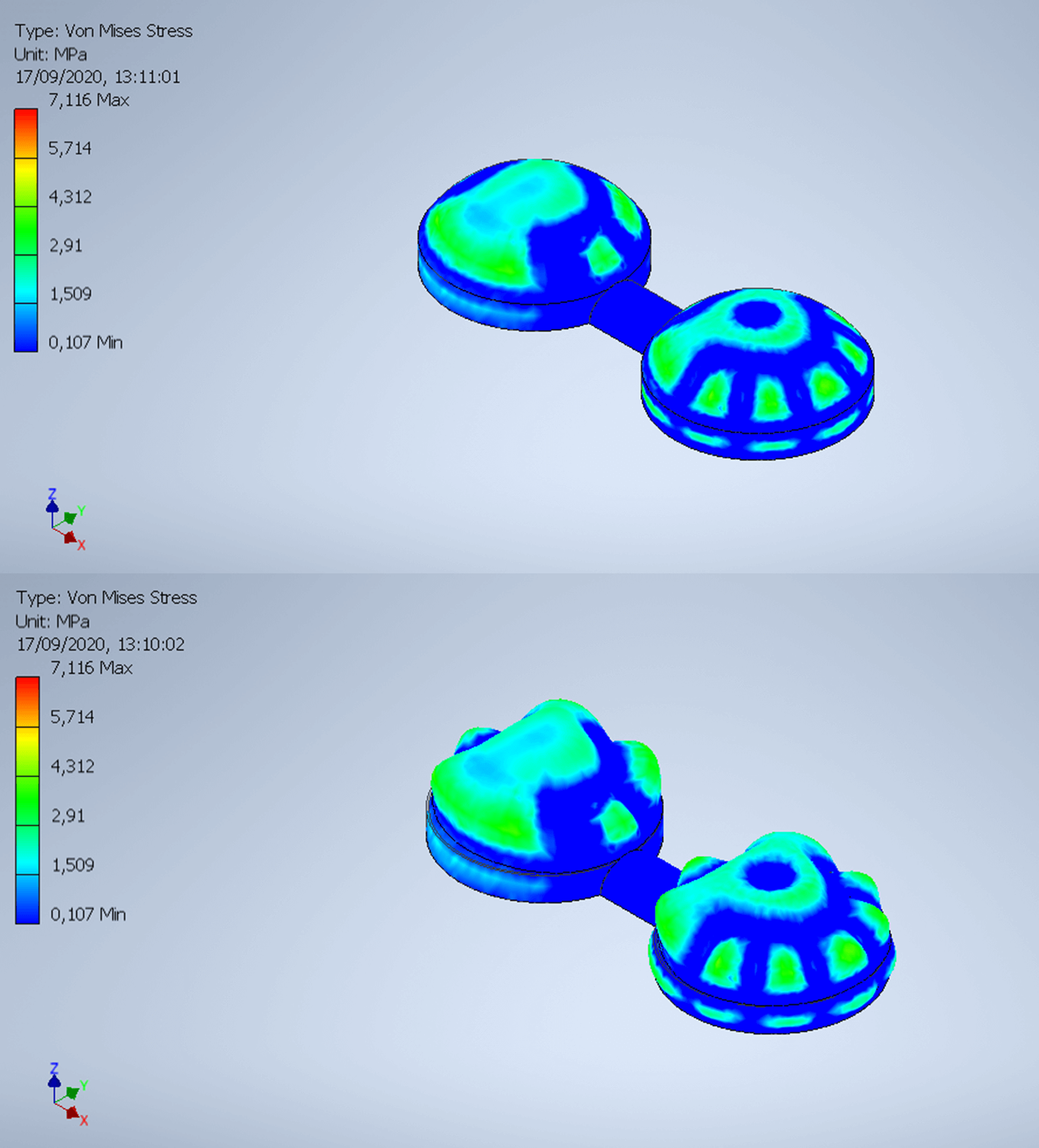
As expected, the module presents bigger challenges in the areas without interior walls. When the most severe action is applied, the material used continues to show resistant capacity. We can conclude that the mixture of materials used is able to withstand the most severe actions on Mars.
Sources:
BANERDT, W. Bruce, et al. Initial results from the InSight mission on Mars. Nature Geoscience, 2020, 1-7.
LE FEUVRE, Mathieu; WIECZOREK, Mark A. Nonuniform cratering of the Moon and a revised crater chronology of the inner Solar System. Icarus, 2011, 214.1: 1-20.
COUGHLIN, Natalie, et al. Development and Mechanical Properties of Basalt Fiber-Reinforced Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene for In-Space Manufacturing Applications. Journal of Composites Science, 2019, 3.3: 89.
WAIT, Taylor. Development of Material for 3D Printed Habitats with Extraplanetary Applications. 2018.
WAN, Lin; WENDNER, Roman; CUSATIS, Gianluca. A novel material for in situ construction on Mars: experiments and numerical simulations. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 120: 222-231.